
Solar Cell Sizes, Types, Efficiency, and Applications: Complete 2025 Guide
Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has evolved rapidly over the past decades. From early 100–125 mm cells to today’s large-format 210 mm high-efficiency cells, manufacturers continuously improve performance, reduce costs, and enhance scalability. Understanding solar cell size, type, efficiency, and application is essential for selecting the right solar panels for residential, commercial, and utility-scale projects.
At FOR LEAVES LTD, we specialize in customized solar panels and PV solutions for over 16 years, providing reliable products and design references to clients worldwide.
In this article, we cover the main solar cell sizes, efficiency ranges, types (monocrystalline vs. polycrystalline, P-type vs. N-type, TOPCon, HJT, and BC cells), and their practical applications.
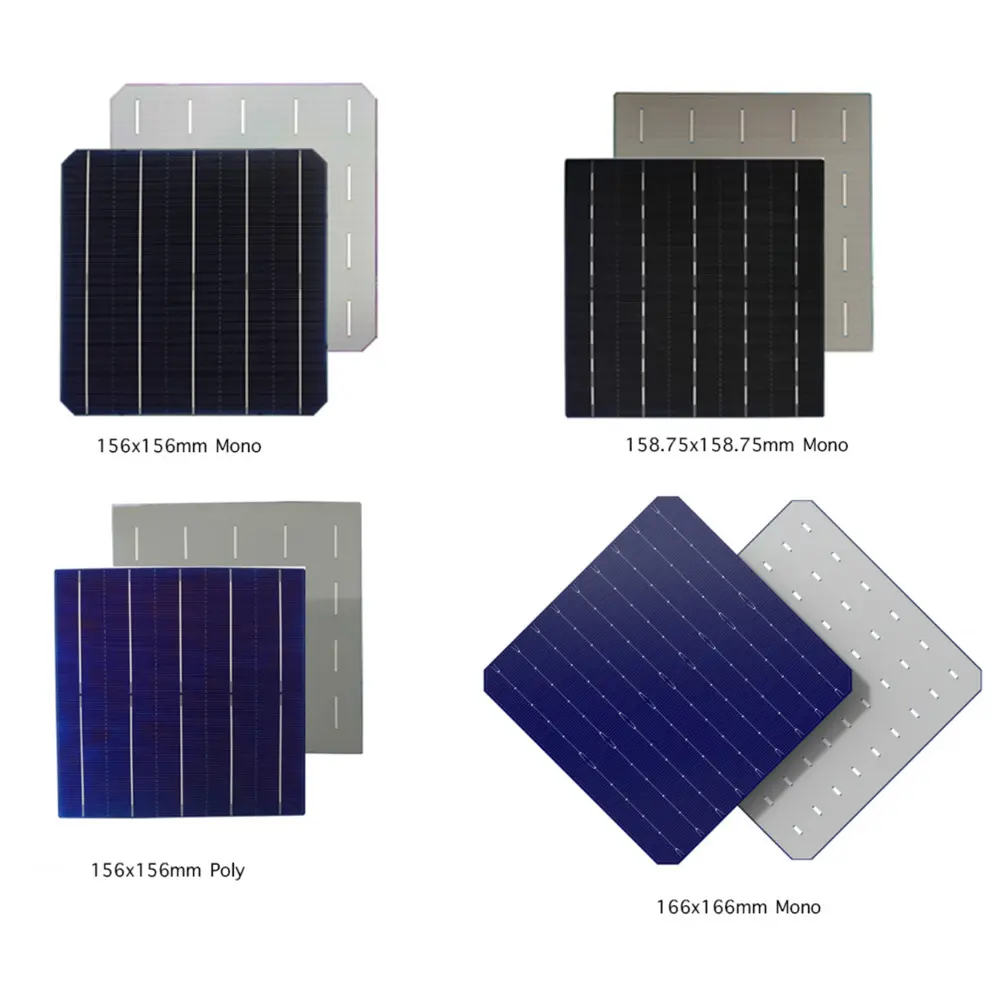


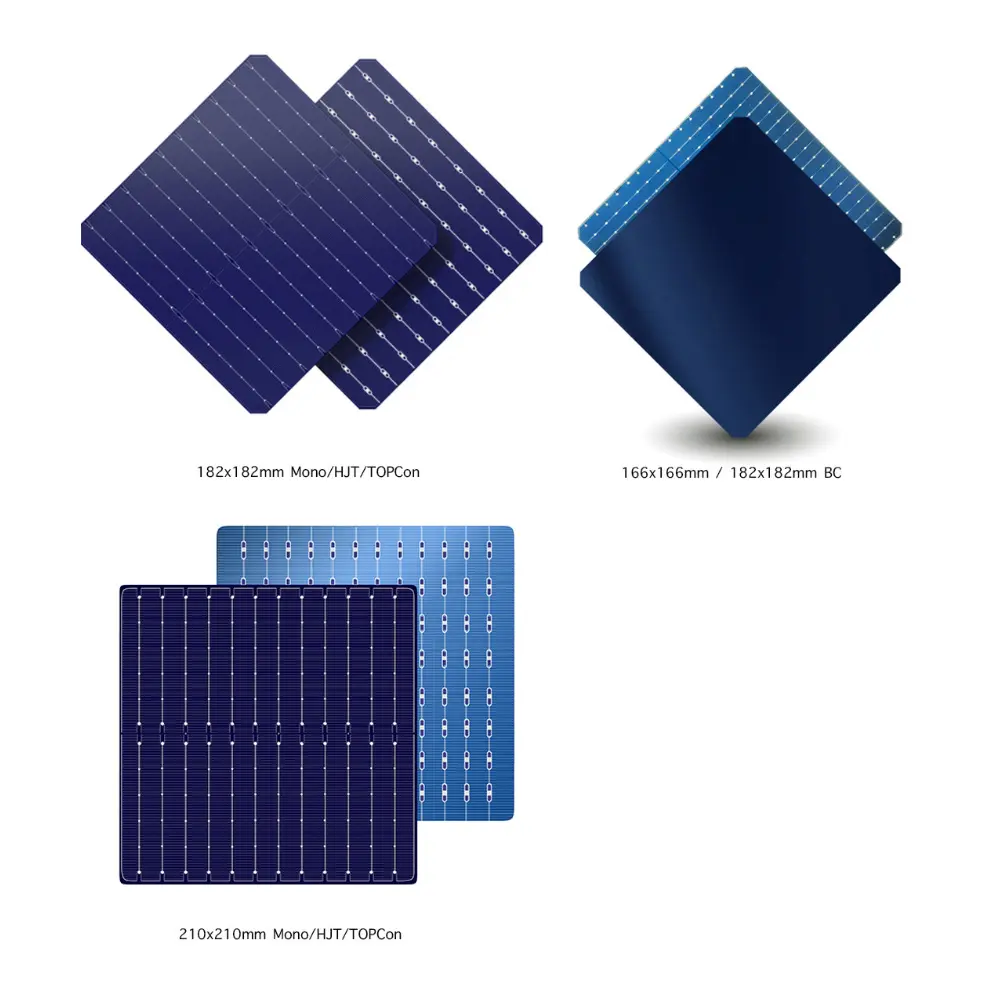
Evolution of Solar Cell Sizes and Technologies
| Cell Size | Standard Name | Type / Technology | Efficiency Range | Approx. Years Used | Typical Module Power | Typical Applications |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100–125 mm | Early cells | Mono / Poly | 12–20% | 1970s–2005 | < 200 W | Small custom panels: 0.x ~30 W |
|
| 156 mm × 156 mm | M2 | Mono / Poly | 17–23% / 14–18% | 2005–2018 | 250–320 W | Small custom panels: 0.x ~30 W |
|
| 166 mm × 166 mm | M6 | Mono P-type / N-type / TOPCon / HJT / BC | 19–23% | 2019–2020 | 370–450 W | Standard residential/commercial modules |
|
| 182 mm × 182 mm | M10 | Mono P-type / N-type / TOPCon / HJT / BC | 20–24% | 2021–Present | 500–600 W | Utility-scale & high-power residential/commercial |
|
| 210 mm × 210 mm | M12 | Mono P-type / N-type / TOPCon / HJT | 21–25% | 2021–Present | 600–700 W+ | Ultra-large high-power modules |
|
Key Trends in Solar Cell Technology
-
Efficiency Improvements
-
P-type Mono PERC: 20–23% efficiency
-
N-type TOPCon / HJT: 22–25% efficiency
-
BC cells: 23–25% efficiency
-
-
Busbar and Thickness Trends
-
Multi-busbar (MBB) design is mainstream; 9–12 busbars common
-
Wafer thickness: 150–170 µm; N-type may be thinner 130-150µm
-
-
Market Trends
-
P-type remains in use but is gradually replaced by N-type TOPCon/HJT in utility-scale projects
-
BC cells can be applied in both large high-power modules and custom small solar panels, including very low-power designs (~5 mA) via SMT assembly
-
Applications of Different Solar Cell Sizes
-
Small cells (125 mm, 156 mm, BC cells)
-
Ideal for custom small solar panels with power from sub-watt to ~30 W
-
Applications:
-
IoT sensors and devices
-
Solar garden/path lights
-
Mini solar chargers and battery trickle charging
-
-
BC cells can also be used via SMT technology to make ultra-small solar panels (e.g., 5 mA output)
-
-
Large cells (166 mm, 182 mm, 210 mm)
-
Suitable for high-power solar panels and standard PV modules
-
Typical power: 30 W–700 W+ depending on cell size and module design
-
Applications:
-
Residential rooftops
-
Commercial PV systems
-
Utility-scale ground-mounted solar farms
-
-
Key takeaway:
-
Small size cells are best for custom, low-power applications, while big size cells focus on high-efficiency, high-power standard modules.
-
BC cells are versatile and can serve both ultra-small and high-power panel applications.
Summary
-
Solar cell sizes evolved from 125 mm to 210 mm in less than two decades.
-
Efficiency has improved from ~12–15% to 25%, depending on technology and cell type.
-
Mono-crystalline cells dominate the market; poly-crystalline has mostly phased out.
-
Advanced technologies such as N-type TOPCon, HJT, and BC cells provide higher efficiency and energy yield.
-
Choosing the right cell size, type, and technology ensures solar panels meet power requirements, efficiency goals, and cost-effectiveness.
***This document is provided by FOR LEAVES LTD, a company with 16 years of experience in the solar industry. The information is based on our personal knowledge and market observation and is intended for design reference and product knowledge only. It does not represent the entire industry. If any information appears inaccurate or incomplete, please contact us for corrections or clarifications. email: info@forelaves.com






