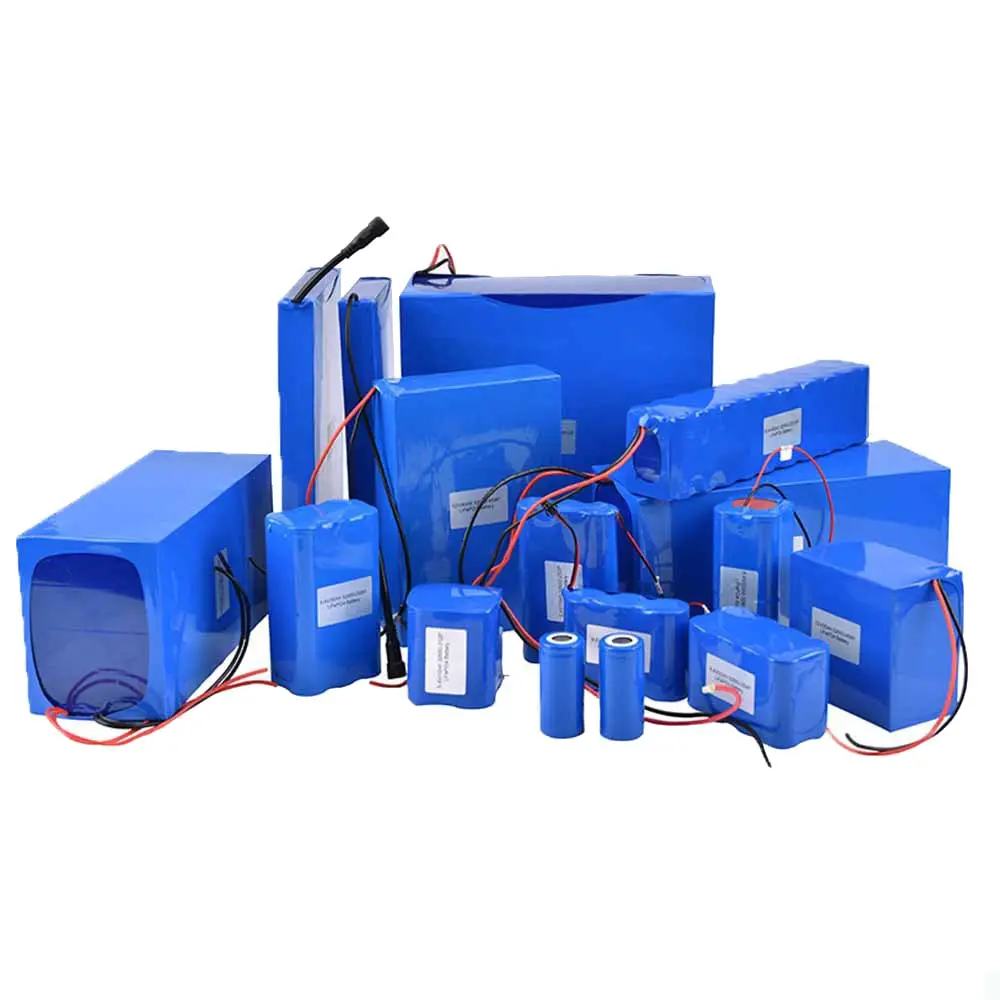
Lithium batteries are a type of battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as the anode/cathode material and a non-aqueous electrolyte solution. Their working principle involves electrochemical reactions and the migration of ions within the electrolyte. Here is a basic understanding of the working principles of lithium batteries:

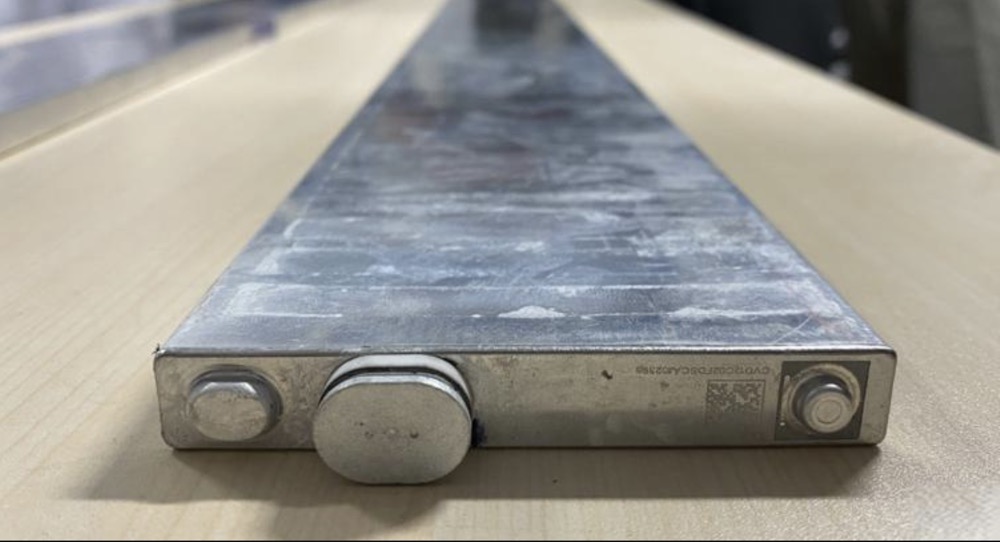
I. Cathode Materials:
The cathode materials of lithium batteries have a decisive impact on the battery's performance. Common cathode materials include:
1. Oxides: such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium nickel oxide (LiNiO2), lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), etc.
2. Phosphates: such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), which has high safety and a long lifespan.
3. Transition metal oxides: such as cobalt oxide (Co3O4), nickel oxide (NiO), etc.
4. Composite materials: such as polyanionic oxides (NMC), multielement salts (OLC), etc.
II. Lithium Battery Packaging types:
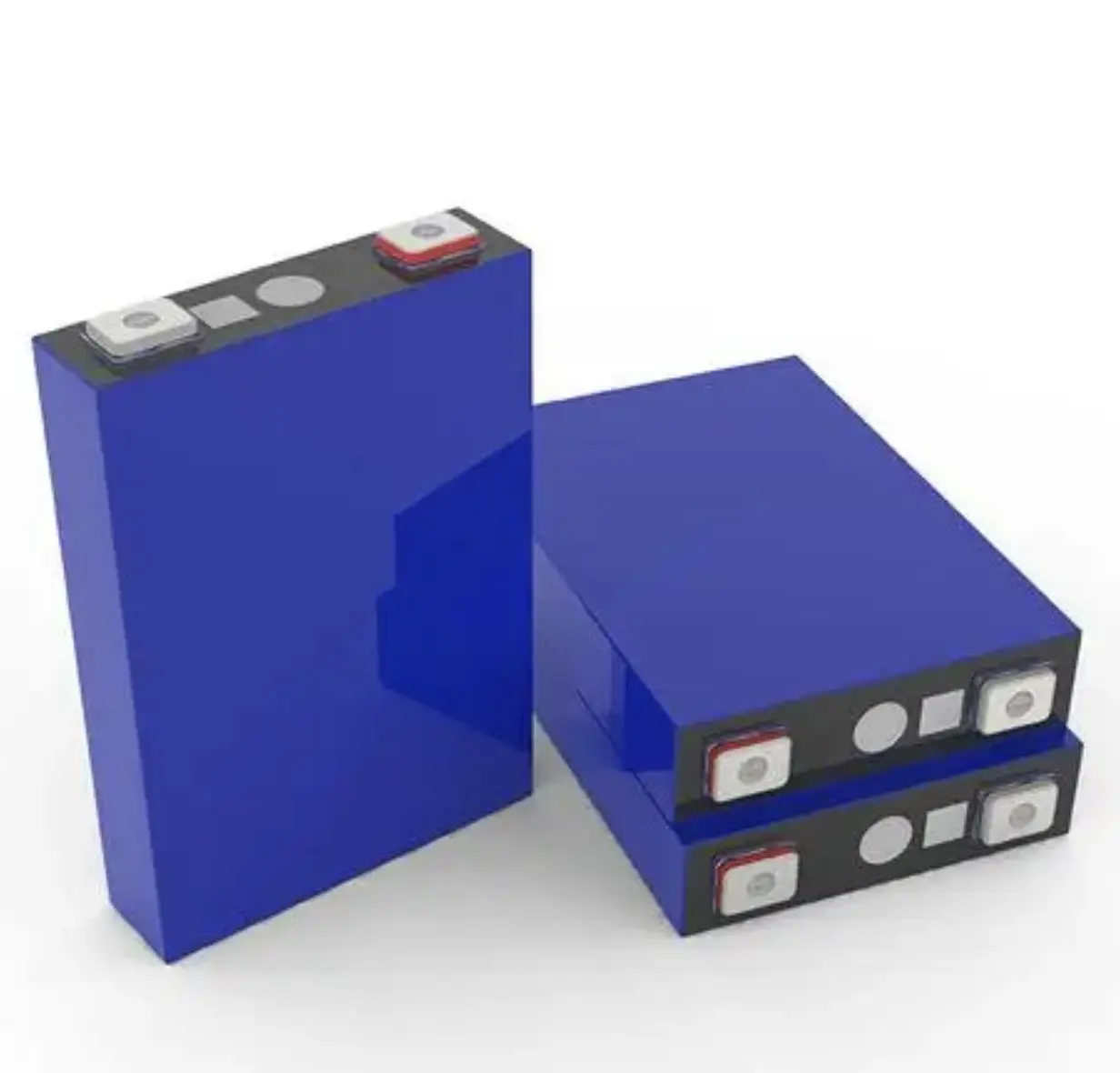
The packaging forms of lithium batteries mainly include:1. Prismatic: Encased in hard metal substances (such as aluminum alloy, stainless steel), using winding or stacking processes internally.

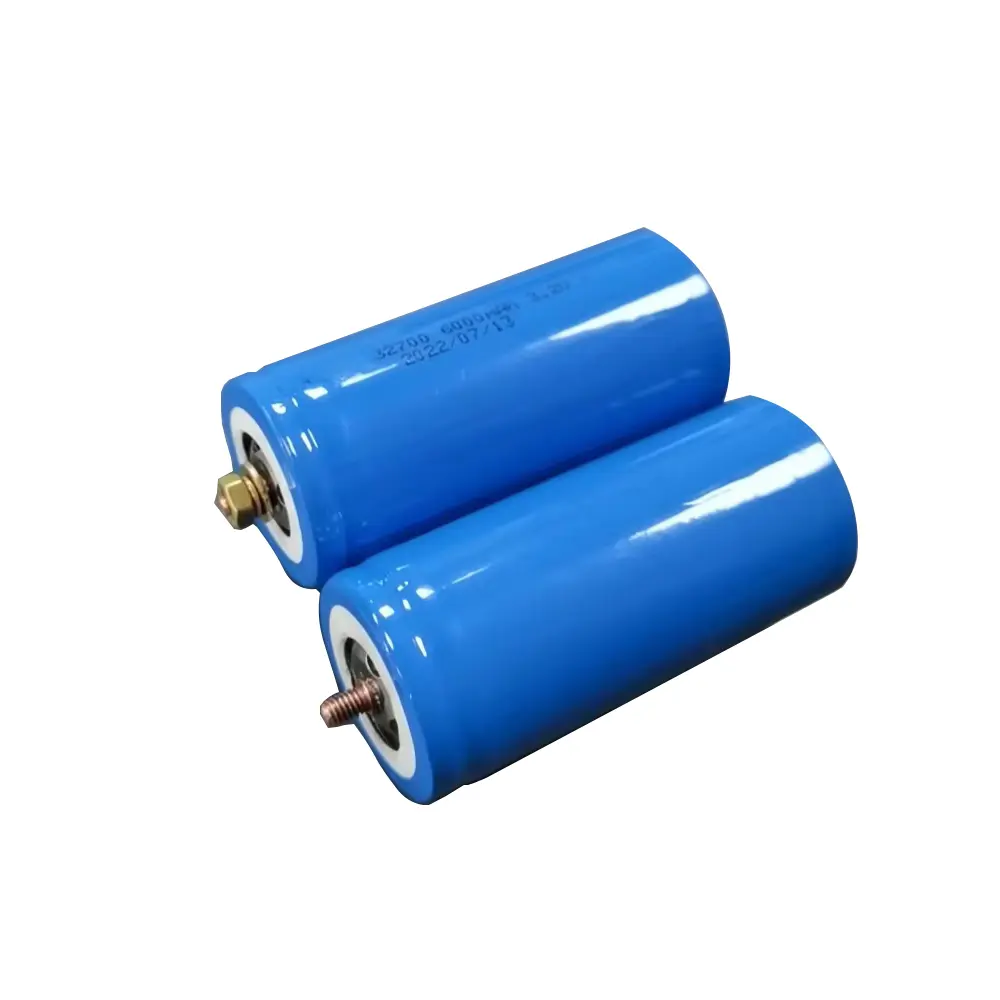
2. Cylindrical: Mainly steel-shell cylinders, with high capacity and stable output voltage.

3. Soft pack: The outer packaging is aluminum-plastic film, which is actually a type of prismatic battery. In the market, aluminum-plastic film packaging is customarily called a soft pack, and some people refer to soft pack batteries as polymer batteries.
III. High and Low-Temperature Lithium Batteries:
The operating temperature range of lithium batteries is usually from -20°C to 60°C, but there are also some batteries with special requirements.
1. Low-temperature lithium batteries: The operating temperature can be below -20°C, such as -40°C low-temperature polymer batteries. The better the low-temperature capability of the battery, the worse its high-temperature performance, so many companies have developed wide-temperature low-temperature batteries.
2. High-temperature lithium batteries: The operating temperature exceeds 60°C, but at high temperatures, lithium batteries risk overheating, burning, and exploding.
IV. Classification of Lithium Battery Charging Rates:
The rate of lithium batteries refers to the battery's discharge rate, i.e., the ratio of the current that the battery can output within a certain time to its rated capacity.
1. Low-rate lithium batteries: Usually, the rate is below 1C, characterized by large capacity, long life, and wide applicability.
2. Medium-rate lithium batteries: The rate is between 1C-3C, with small size, light weight, and stable output voltage, suitable for some special fields.
3. High-rate lithium batteries: The rate is above 3C, commonly used in high-performance electronic products such as power tools, drones, etc., characterized by large output current and excellent fast-charging performance.
V. Classification of Lithium Batteries by Fast Charging:
Lithium batteries can be divided into ordinary lithium batteries and fast-charging lithium batteries according to the charging rate. Fast-charging lithium batteries usually have a higher charging rate, able to be fully charged in a short time, suitable for occasions with high requirements for charging time. Ordinary lithium batteries have a slower charging rate and need more time to be fully charged.
Among fast-charging lithium batteries, they can be classified according to specific fast-charging technologies. For example, some fast-charging lithium batteries use pulse charging technology, which achieves rapid charging through high-current charging in a short time. Additionally, some fast-charging lithium batteries use intelligent charging technology, which controls the charging current and voltage to avoid battery overheating and damage, thus achieving safe and rapid charging.







